Patellofemoral Braces For Managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), commonly referred to as "runner’s knee," is a condition that affects the front of the knee and causes discomfort around the patella (kneecap). Often resulting from repetitive strain or improper alignment, PFPS can lead to pain during activities like walking, running, or even sitting for extended periods.
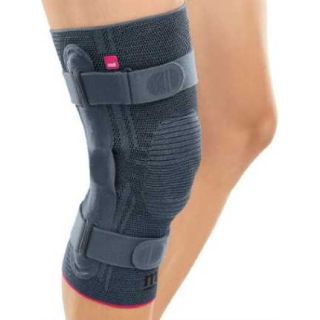
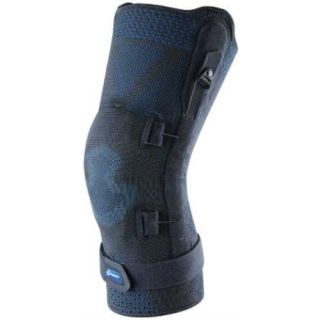
One common method for managing this condition is using a patellofemoral brace, also commonly referred to as patellofemoral knee brace or patellofemoral syndrome brace. A patellofemoral pain syndrome brace's aim to stabilize the knee, reduce stress on the joint, and improve overall function.
Understanding Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)
To fully appreciate how patellofemoral braces work, it’s important to first understand the mechanics of PFPS. The knee is a complex joint where the femur (thigh bone) meets the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap) rests within the patellar groove of the femur. The patella is crucial in helping the quadriceps muscle extend the knee, facilitating movements like running and squatting. However, when the patella doesn’t move properly in the groove, it can create stress and irritation in the surrounding tissues.
In cases of PFPS, this misalignment is often due to overuse, muscle imbalances, or poor biomechanics, all of which can increase pressure on the kneecap. People with PFPS may experience pain while climbing stairs, sitting for long periods, or performing any activity that involves knee bending. By using a patellofemoral brace, individuals with PFPS knee injury can often reduce their pain and discomfort.
The Role of a Brace For Patellofemoral Pain
A patellofemoral brace plays an essential role in addressing the root cause of PFPS by helping to stabilize the kneecap, relieve pressure on the joint, and provide additional support. These braces, made from lightweight and flexible materials like neoprene, are specifically designed to offer support without restricting mobility.
- Stabilizing the Patella: A key feature of patellofemoral braces is their ability to stabilize the patella and encourage proper alignment within the femoral groove. Many braces include lateral buttresses or straps that apply gentle pressure around the kneecap to prevent it from shifting out of position. This helps encourage the patella to track properly.
- Compression for Support: Compression provided by the brace can help reduce swelling and inflammation, two common symptoms of PFPS. By compressing the tissues around the knee, the brace can enhance the body’s ability to sense movement (proprioception), contributing to better stability and knee support during physical activity.
- Redistributing the Load: A patellofemoral brace redistributes some of the pressure placed on the knee joint during movement, easing strain on the cartilage and tendons. This load redistribution helps reduce pain and discomfort, especially when engaging in weight-bearing activities like walking or climbing stairs.
- Pain Management: Through a combination of patellar stabilization, compression, and load redistribution, patellofemoral braces are effective at managing pain for individuals with PFPS. This improved alignment reduces stress on the knee, helping people remain active without worsening their condition.
Types of Patellofemoral Braces
Patella knee braces come in a variety of designs, each tailored to specific needs and levels of support. Choosing the right brace depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s activity level. Below are some of the most common types of patellofemoral braces:
- Sleeve Braces: These simple, slip-on braces fit snugly around the knee and provide mild compression and support. Made from materials like elastic or neoprene, knee sleeves with an open patella design are ideal for individuals with mild to moderate PFPS who need basic support without restricting movement.
- Hinged Braces: Hinged braces offer additional support by incorporating metal or plastic hinges along the sides of the knee. These braces are recommended for individuals with more severe cases of PFPS or those recovering from surgery. The hinges prevent side-to-side movement while still allowing the knee to bend and extend normally.
- Patellar Straps: Patellar straps, also called knee bands, are simple straps worn just below the kneecap. By applying targeted pressure to the patellar tendon, these straps help alleviate pain and reduce strain on the knee. Patellar straps are popular among athletes because they are lightweight and allow for full mobility.
- Wraparound Braces: These braces have adjustable straps that allow for a customized fit. Unlike sleeve braces, wraparound braces can be easily adjusted to provide more or less compression based on the individual’s needs. They offer a versatile solution for individuals with varying levels of PFPS severity.
The Effectiveness of Patellofemoral Braces
Research supports the effectiveness of patellofemoral braces in reducing pain and improving function for individuals with PFPS. While more studies are needed to fully understand the exact mechanisms, the general consensus is that these braces play a crucial role in stabilizing the patella and reducing stress on the knee.
- Reducing Pain: One of the most immediate benefits of patellofemoral braces is pain relief. A 2018 study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy found that individuals with PFPS who wore a patellofemoral brace experienced a significant decrease in pain during activities like running, squatting, and stair climbing. The study concluded that patellofemoral braces are an effective conservative treatment for PFPS.
- Improved Knee Function: In addition to relieving pain, patellofemoral braces have been shown to improve overall knee function. A 2016 review in Sports Medicine highlighted that individuals using these braces reported enhanced knee function, especially during activities that involve bearing weight. This improved function is likely due to the brace’s ability to enhance proprioception and joint stability.
- Preventing Further Injury: For individuals with recurring PFPS, patellofemoral braces can help prevent future injuries by providing consistent support. This is especially important for athletes, who may be prone to repeated stress on the knee. Proper patellar alignment reduces the risk of long-term damage and promotes healthier movement patterns.
Limitations and Considerations of Patellofemoral Braces
While patellofemoral braces offer many benefits, there are some limitations to their effectiveness. For the best results, braces must be used correctly and in conjunction with other treatment methods, such as physical therapy.
Proper Fit is Crucial: If a brace doesn’t fit properly, it won’t provide the necessary support, and could even worsen the symptoms. A healthcare professional should always be consulted to ensure the correct brace type and size are chosen for the individual’s specific needs.
Temporary Symptom Relief: While wearing a knee brace can reduce knee pain, they don’t address the underlying causes of PFPS, such as muscle imbalances or improper biomechanics. Long-term management of PFPS often involves physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee and correct movement patterns.
Activity-Specific Use: The type of patellofemoral brace needed may vary depending on the individual’s activity level. For example, athletes involved in high-impact sports might need a more supportive brace, such as a hinged or wraparound brace, to adequately protect the knee during intense movements.
A knee brace for patellofemoral pain syndrome is a valuable tool in the management of patellofemoral knee pain. By stabilizing the patella, providing compression, and redistributing pressure, these types of braces help alleviate pain and improve knee function.
While they offer effective symptom relief, braces should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes addressing the root causes of PFPS through physical therapy. For individuals suffering from PFPS, working with a healthcare professional to choose the right brace and treatment plan is essential to achieving the best possible outcome.
 Details$87.99 $73.99
Details$87.99 $73.99 Details$176.99 $116.99
Details$176.99 $116.99 Details$73.99 $62.99
Details$73.99 $62.99 Details$27.99 $20.79
Details$27.99 $20.79 Details$249.99 $195.99
Details$249.99 $195.99 Details$89.99 $78.99
Details$89.99 $78.99 Details$79.99 $70.99
Details$79.99 $70.99 Details$360.00 $360.00
Details$360.00 $360.00 Details$94.99 $86.99
Details$94.99 $86.99 Details$120.00 $120.00
Details$120.00 $120.00 Details$79.99 $72.99
Details$79.99 $72.99 Details$156.99 $146.99
Details$156.99 $146.99